What is Terpineol? Benefits, Uses and Effects
Terpineol occurs naturally in more than 150 plants, including cannabis, lime blossoms, lilacs, eucalyptus, and pine trees.
Plants that contain high levels of terpineol have been used as a form of natural medicine for centuries.
Lime blossom, for example, was used in European traditional medicine as a treatment for coughs, colds, and flu. When brewed into a tea, it gives off a very soft, sweetly-scented aroma, nicknamed the “nectar of kings.”
What is Terpineol?
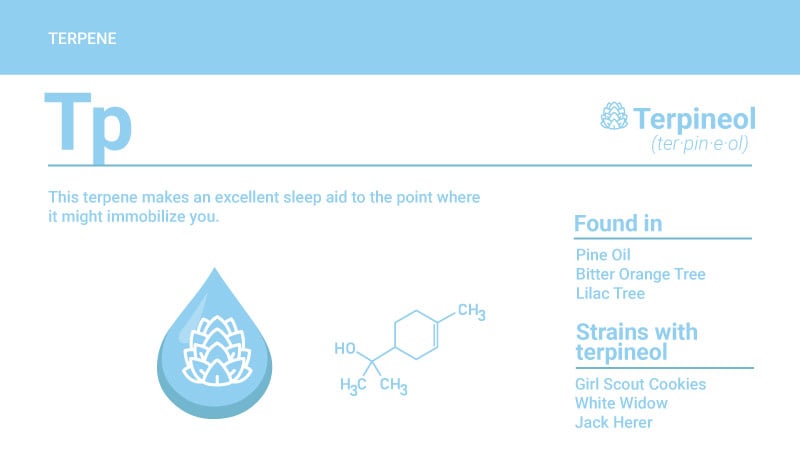
Terpineol is a common terpene found in cannabis plants. Technically, terpineol is terpene alcohol — rather than just a terpene. This means it has the same chemical structure as a terpene and shares similar characteristics. The only difference is that terpene alcohol has a distinct oxygen-containing functional group called hydroxyl sticking off one side of the molecule.
This gives terpineol some distinct characteristics from other terpenes. If you’re just getting started with terpenes, be sure to check out our other best-selling terpene profiles at Finest Labs to learn more.
There are four different terpineol isomers in existence:
1. α-Terpineol
Alpha-terpineol, or α-Terpineol, is terpene alcohol found in many natural oils such as pine and petitgrain (an oil from the bitter orange tree). It’s the most common terpineol isomer found in cannabis.
- Water solubility: 2.4 g/L
- CAS Reg. No: 98-55-5
- Boiling point: 426.2°F
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
2. β-Terpineol
Beta-terpineol, or β-Terpineol, is tertiary alcohol produced naturally in the volatile fraction of various plants. You might find this isomer listed in cannabis products, but it’s far less common than the alpha isomer.
- Water solubility: 2.42 g/L
- CAS Reg. No: 138-87-4
- Boiling point: 426.2°F
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
3. Γ-Terpineol
Gamma-terpineol, or Γ-Terpineol, is a p-menthane monoterpenoid. The only difference between gamma and beta terpineol is the location of a double-bond.
- Water solubility: 3.68 g/L
- CAS Reg. No: 586-81-2
- Appearance: Colorless-pale yellow; clear, viscous liquid
3. Terpinen-4-ol
Terpinen-4-ol is a terpineol isomer with the chemical formula C10H18O. It’s extracted from the leaves, branches, and bark of the Melaleuca alternifolia tree and is a primary component of tea tree oil.
- Water solubility: 2.5 mg/mL
- CAS Reg. No: 562-74-3
- Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow liquid
What Are the Potential Benefits of Terpineol?
Terpineol, or a-terpineol (alpha-terpineol), may offer the following therapeutic effects:
- Reduce inflammation
- Act as an antioxidant
- Help slow the growth of abnormal cells
- Kills microbes
- May boost mood
- May help reduce stress
- Alleviates certain types of pain
- Supports gastrointestinal health
Studies are limited, and terpineol is not approved for medicinal purposes. Anyone using it for potential benefits needs to use it with precaution and consult with a health practitioner first.
How to Use Terpineol
Pure terpineol has many uses. It’s a great addition to cosmetic formulas centered around alleviating inflammation or irritation, and its floral aroma is an excellent addition to vape oils or distillate blends.
Like any concentrated terpene, you can’t use terpineol in its pure form — you must dilute it first. Aim to dilute terpineol to around 5% or less of the volume of the final product. Here are some of the primary ways terpineol is used today.
1. Add Terpineol to Cosmetic Products
Many people value terpineol because of its enticing, refreshing fragrance, healing properties, and gentleness on the skin.
One common use is to add terpineol isolates to essential oils, salves, and lotions for aromatherapy. The skin contains plenty of cannabinoid receptors, and it can absorb products fairly quickly into the body. Topicals are an effective way to reap the benefits that terpineol has to offer. Undiluted terpineol can irritate the skin; it’s best to use it when combined with a carrier oil or another skin product.
2. Add Terpineol to Vape Products
Some cannabis strains are high in terpineol. Smoking or vaping these terpineol-rich strains can provide the benefits in combination with the full spectrum of other terpenes and cannabinoids, otherwise known as the entourage effect.
3. Add Terpineol for Flavor
Terpineol is a common flavoring agent in baked goods, condiments, candies, beverages, dairy products, and chewing gum. Not all terpineol isolates are safe for human consumption; therefore, if you plan to use terpineol in this manner, you’ll have to pay close attention to labels and seller information to ensure the product is clean and safe to ingest.
4. Using Terpineol in Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy is a traditional medicine that uses essential oils as a therapeutic agent to treat various ailments. Aromatherapy uses different tools and methods of inhalation, topical applications, massage, and bath additives to help these valuable oils penetrate the skin’s surface.
A) Terpineol in Cosmetic Aromatherapy
In cosmetic aromatherapy, special blends of essential oils are used on the face and body, and sometimes the hair. These products are favored for their natural cleansing, moisturizing, toning, and keeping the skin healthy. A full-body bath or foot bath is an easy and soothing way to experience the revitalizing effects of aromatherapy. A few drops of oils containing terpineol in a warm foot or regular bath are all you need to help melt away stress. You can also get aromatherapy facials, which involve the use of a variety of essential oils. Essential oils are chosen based on your specific skin type and work to promote healthy skin.
B) Terpineol in Massage Therapy
Aromatherapy massage helps in general relaxation, reducing anxiety, managing pain, and enhancing mood. These are the typical benefits one would expect from a massage therapy session. Adding essential oils is thought to enhance the benefits experienced.
Terpineol oils penetrate the skin and help ease tension, inflammation, and pain. Always mix terpenes with a type of carrier oil. You can use jojoba, almond, or grapeseed as a massage medium. The healing touch of massage therapy can relax your mind and body, and the essential oils with terpineol help you feel calmer and more relaxed.
How Do You Pronounce Terpineol?
It looks like it should be pronounced “tur·pin·e·all,” though the actual pronunciation is “tur·puh·naal.”
What Does Terpineol Smell Like?
Generally, terpineol has citrusy, sweet aromas and flavors reminiscent of oranges, grapefruits, tangerines, and a subtle hint of fresh herbs, earth, or freshly cut wood. Since there are many different types of terpineol isomers, there are slight differences in what they smell like. Depending on which isomer you’re dealing with, you’ll notice some subtle differences in the aromas mentioned above.
For example, alpha-terpineol has a light, pleasant odor, similar to lilac and peach. Beta-terpineol has a woodsy scent; gamma-terpineol has more of a citrus aroma, and terpinen-4-ol has mild earthy notes with a woody odor.
Which Cannabis Strains Are High in Terpineol?
Cannabis with high levels of pinene typically has some terpineol too. Some say cannabis high in terpineol has deeply relaxing, sedating effects — but more research is needed to understand this effect in more detail. Not only do cannabis strains rich in terpineol feel good, but they also smell incredible. Terpineol is responsible for those intense pine and citrus scents associated with your favorite buds.
Unless you’re entirely new to using cannabis, you’ve most likely tried at least one strain that contains terpineol. This terpene tends to be more prominent in sativa and hybrid strains than indica or ruderalis cannabis. Terpineol is common in the following strains:
- Jack Herer
- Girl Scout Cookies
- Blue Dream
- White Widow
- OG Kush
- Skywalker OG
- Fire OG
- Jack Flash
Most strains that contain a lot of pinenes also contain high amounts of terpineol — so if your buds smell like pine, there’s a good chance it’s high in terpineol as well.
Chemical Structure of Terpineol
Terpineol is classified as a monoterpene, which is the most common class of terpenes. This makes terpineol structurally related to other compounds, including pinene, borneol, camphene, citral, P-cymene, delta-3-carene, eucalyptol, fenchol, geraniol, geranyl-acetate, isopulegol, limonene, linalool, myrcene, ocimene, phellandrene, sabinene, terpinolene, and many others.
Terpineol Specs:
- IUPAC Name: 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)propan-2-ol
- Type of terpene: Monoterpene
- Molecular Formula: C10H18O
- Molecular Weight: 154.25
- Boiling Point: 219ºC
Key Takeaway: What is Terpineol?
Terpineol is one of the many terpenes in cannabis and occurs in various plants, herbs, and spices. It’s chemically classified as a terpene-alcohol. This terpene has a pleasant but complex fragrance. It’s woodsy, earthy, citrusy, and floral. Depending on the isomer of terpineol, there may be some subtle differences in the aroma.
References:
- Held, S., Schieberle, P., & Somoza, V. (2007). Characterization of α-terpineol as an anti-inflammatory component of orange juice by in vitro studies using oral, buccal cells. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 55(20), 8040-8046.
- de Oliveira MG, Marques RB, de Santana MF, Santos AB, Brito FA, Barreto EO, De Sousa DP, Almeida FR, Badauê-Passos D Jr, Antoniolli AR, Quintans-Júnior LJ. α-terpineol reduces mechanical hypernociception and inflammatory response. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012 Aug;111(2):120-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2012.00875.x. Epub 2012 Apr 11. PMID: 22380944. [1]
- Bicas JL, Neri-Numa IA, Ruiz AL, De Carvalho JE, Pastore GM. Evaluation of the antioxidant and antiproliferative potential of bioflavors. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011 Jul;49(7):1610-5. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.04.012. Epub 2011 Apr 19. PMID: 21540069.
- Hassan SB, Gali-Muhtasib H, Göransson H, Larsson R. Alpha terpineol: a potential anticancer agent which acts through suppressing NF-kappaB signaling. Anticancer Res. 2010 Jun;30(6):1911-9. PMID: 20651334. [2]
- Park SN, Lim YK, Freire MO, Cho E, Jin D, Kook JK. Antimicrobial effect of linalool and α-terpineol against periodontopathic and cariogenic bacteria. Anaerobe. 2012 Jun;18(3):369-72. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2012.04.001. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PMID: 22537719. [3]
- Vieira G, Cavalli J, Gonçalves ECD, Braga SFP, Ferreira RS, Santos ARS, Cola M, Raposo NRB, Capasso R, Dutra RC. Antidepressant-Like Effect of Terpineol in an Inflammatory Model of Depression: Involvement of the Cannabinoid System and D2 Dopamine Receptor. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(5):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050792 [4]
- Soleimani M, Sheikholeslami MA, Ghafghazi S, Pouriran R, Parvardeh S. Analgesic effect of α-terpineol on neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in rat sciatic nerve: Involvement of spinal microglial cells and inflammatory cytokines. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019;22(12):1445-1451. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2019.14028 [5]
- Souza R, Cardoso M, Menezes C, Silva J, De Sousa D, Batista J. Gastroprotective activity of α-terpineol in two experimental gastric ulcer models in rats. Daru. 2011;19(4):277-281.